共计 3890 个字符,预计需要花费 10 分钟才能阅读完成。
装饰器模式
专业描述
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的类的一个包装。
这种模式创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,并在保持类方法签名完整性的前提下,提供了额外的功能。
我们通过下面的实例来演示装饰器模式的用法。其中,我们将把一个形状装饰上不同的颜色,同时又不改变形状类。
普通描述
动态地给某个对象添加一些额外的属性或者方法;在不改变原对象的基础上,通过对其进行包装扩展,使原有对象可以满足用户的更复杂需求,而不会影响从这个类中派生的其他对象。
UML(来源网络)
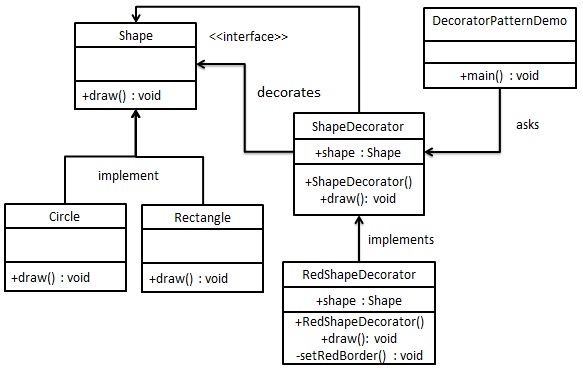
优缺点
优点
- 装饰类和被装饰类相互解耦,可以独立扩展。
- 装饰模式是继承的替代方案,但灵活性要强于继承。
- 增强给对象指派职责的灵活性。通过改变链内的成员或者调动它们的次序,允许动态地新增或者删除责任。
缺点
- 多层装饰比较复杂,会加大系统的复杂程度。
经典场景
- ES7 Decorator(重点最后讲解)
代码实现
案例以 java 设计模式中的经典为例,采用 typeScript 重构
- 创建一接口和基于接口的实体类
interface Shape{draw() : void; }
class Rectangle implements Shape{
public draw(){
console.log("Rectangle")
}
}
class Circle implements Shape{
public draw(){
console.log("Circle");
}
}
2. 定义装饰器抽象类 abstract class ShapeDecorator implements Shape{
protected constructor(protected decoratedShape: Shape){}
draw(){this.decoratedShape.draw()
}}
3. 实现一个基于 ShapeDecorator 抽象类的装饰器 class RedShapeDecorator extends ShapeDecorator {
constructor(decoratedShape : Shape) {super(decoratedShape);
}
public draw() {this.decoratedShape.draw();
this.setRedBorder(this.decoratedShape);
}
private setRedBorder(decoratedShape: Shape){console.log("Border Color: Red");
}}
## 代码测试
### 测试用例
let circle = new Circle();
let redCircle = new RedShapeDecorator(new Circle());
let redRectangle = new RedShapeDecorator(new Rectangle());
①
circle.draw();
② 采用了 RedShapeDecorator 进行装饰
redCircle.draw();
③ 采用了 RedShapeDecorator 进行装饰
redRectangle.draw();
### 测试结果 ①的操作结果
Circle
②的操作结果
Circle
Border Color: Red
③的操作结果
Rectangle
Border Color: Red
Process finished with exit code 0
## ES7 中的装饰器
### class 装饰器
给 ES7DecoratorUserClass 扩展一个国籍属性,默认为 China(无参数装饰器)
#### 代码实现
定义 ES7DecoratorUserClass1
export class ES7DecoratorUserClass1 {}
定义 checkNationality1 装饰器
function checkNationality1(constructor: Function) {
constructor.prototype.nationality = 'China';
}
使用装饰器
@checkNationality1
export class ES7DecoratorUserClass1 {}
#### 代码测试 test('normalClassNoParams', t => {
const normalClassNoParams = new ES7DecoratorUserClass1();
t.is(normalClassNoParams.nationality, 'China')
});
给 ES7DecoratorUserClass 扩展一个国籍属性,参数指定 (有参数装饰器)
#### 代码实现
定义 ES7DecoratorUserClass1
export class ES7DecoratorUserClass2 {}
定义 checkNationality1 装饰器
function checkNationality2(nationality: string) {
return function (target: Function) {
target.prototype.nationality = nationality;
};
}
使用装饰器
@checkNationality2('Japan')
export class ES7DecoratorUserClass2 {}
#### 代码测试 test('normalClassHaveParams', t => {
const normalClassHaveParams = new ES7DecoratorUserClass2();
// @ts-ignore
t.is(normalClassHaveParams.nationality, 'Japan')
});
### function 装饰器
利用装饰器实现一个请求次数记录的功能,每请求一次,执行次数加一
#### 代码实现 // 类装饰器
export function userController(target) {
console.log('userController already init success')
}
@userController
export class UserController {
public num: number;
constructor() {
}
// 定义一个获取用户 ids 的方法
@recordLogger1
public getUserIdsList(): Array<number> {return [1,2,3]
}
// 定义一个获取用户角色的方法
@recordLogger2
public getUserRoleList(): Array<string> {return ['member', 'vip']
}
@recordLogger1
static getControllerConfig(): any {
return {ISROOT: true}
}
getRequestNUm(): number {return requestNum;}}
#### 代码测试 // function 装饰器 初始化
test('normalFunction', t => {
const normalFunction = new UserController();
t.deepEqual(normalFunction.getUserIdsList(), [1,2,3]);
t.pass()
});
// function 装饰器 日志记录器
test('normalFunctionLogger', t => {
const normalFunction = new UserController();
t.deepEqual(normalFunction.getUserRoleList(), ['member', 'vip']);
// 请求次数 1
t.is(normalFunction.getRequestNUm(), 1);
normalFunction.getUserRoleList();
// 请求次数 2
t.is(normalFunction.getRequestNUm(), 2);
console.log(normalFunction.getRequestNUm());
t.pass();});
#### 测试结果
======================================================================
userController already init success // userController 装饰器执行结果
function 日志记录器 // 第一次请求 [recordLogger2 执行]
start request userRoleList
√ normalClassNoParams
√ normalClassHaveParams
√ normalFunction
function 日志记录器 // 第二次请求 [recordLogger2 执行]
start request userRoleList
2
√ normalFunctionLogger
### 装饰器执行顺序
1. 有多个参数装饰器时:从最后一个参数依次向前执行
2. 方法和方法参数中参数装饰器先执行。3. 类装饰器总是最后执行。4. 方法和属性装饰器,谁在前面谁先执行。因为参数属于方法一部分,所以参数会一直紧紧挨着方法执行。